CGLIB动态代理样例
由于CGLIB是JDK之外的东西,因此在使用CGLIB的时候需要引入CGLIB的包(我这里是gradle项目):
dependencies { implementation('cglib:cglib:3.3.0') }
要被代理的类:
package com.example.demo.proxy.cglib;
public class Hello {
public void sayHello(String name) {
System.out.println("Hello " + name);
}
}
一个自定义的方法拦截器,该拦截器实现了net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor接口:
package com.example.demo.proxy.cglib;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class MyMethodInterceptor implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(">>>> Before method invocation");
Object object = proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
System.out.println(">>>> After method invocation");
return object;
}
}
主测试类CglibProxyDemo.java:
package com.example.demo.proxy.cglib;
import net.sf.cglib.core.DebuggingClassWriter;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
/**
* Cglib proxy demo.
* Main implementation steps:
* 1. Implement the net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor interface
* 2. Create Enhancer object(which is used to create proxy object), set target class and callback object.
* 3. Create proxy object by invoke enhancer.create()
* 4. Call method on proxy object
*/
public class CglibProxyDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Generate proxy class under given path
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "out");
//2. Create Enhancer object, which is used to create proxy object.
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(Hello.class); //Set target class
enhancer.setCallback(new MyMethodInterceptor()); //Set callback object
//3. Create proxy by invoke enhancer.create().
Hello helloProxy = (Hello) enhancer.create();
//4. Call method on proxy object.
helloProxy.sayHello("Doris");
}
}
执行结果:
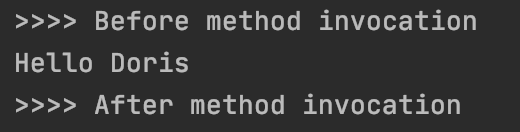
可以看到,原来的Hello.sayHello()方法已经被代理了,加入了调用的前置处理和后置处理。
源码分析
先看看主测试类CglibProxyDemo.java,里面创建了一个enhancer,并且给它设置了superClass和callback两个属性,然后用这个enhancer创建了一个代理对象helloProxy,最后调用了代理对象的sayHello()方法。
创建代理对象 Hello helloProxy = (Hello) enhancer.create();
1.获取Key
代理对象helloProxy通过以下语句创建:
Hello helloProxy = (Hello) enhancer.create();
在Enhancer中:
/**
* Generate a new class if necessary and uses the specified
* callbacks (if any) to create a new object instance.
* Uses the no-arg constructor of the superclass.
* @return a new instance
*/
public Object create() {
classOnly = false;
argumentTypes = null;
return createHelper();
}
在createHelper()中,创建了一个唯一的key,用于在缓存中存取代理类的Class实例,并且立即调用父类AbstractClassGenerator.create(Object key)方法创建代理类的实例:
private Object createHelper() {
preValidate();
//创建key,用于在缓存中存取代理类实例
Object key = KEY_FACTORY.newInstance((superclass != null) ? superclass.getName() : null,
ReflectUtils.getNames(interfaces),
filter == ALL_ZERO ? null : new WeakCacheKey<CallbackFilter>(filter),
callbackTypes,
useFactory,
interceptDuringConstruction,
serialVersionUID);
this.currentKey = key;
//调用父类AbstractClassGenerator.create()创建代理类实例
Object result = super.create(key);
return result;
}
在create()中,会调用内部类ClassLoaderData的get(AbstractClassGenerator gen, boolean useCache)方法获取代理类的Class实例:
protected Object create(Object key) {
try {
ClassLoader loader = getClassLoader();
Map<ClassLoader, AbstractClassGenerator.ClassLoaderData> cache = CACHE;
AbstractClassGenerator.ClassLoaderData data = cache.get(loader);
if (data == null) {
synchronized (AbstractClassGenerator.class) {
cache = CACHE;
//加锁后再试一次,如果还没取到,就创建缓存
data = cache.get(loader);
if (data == null) {
Map<ClassLoader, AbstractClassGenerator.ClassLoaderData> newCache = new WeakHashMap<ClassLoader, AbstractClassGenerator.ClassLoaderData>(cache);
data = new AbstractClassGenerator.ClassLoaderData(loader);
newCache.put(loader, data);
CACHE = newCache;
}
}
}
this.key = key;
//从ClassLoaderData中获取代理类的Class实例
Object obj = data.get(this, getUseCache());
if (obj instanceof Class) {
//获取代理类的实例
return firstInstance((Class) obj);
}
return nextInstance(obj);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Error e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CodeGenerationException(e);
}
}
2.通过Key从缓存中获取Class
在ClassLoaderData中,有个字段generatedClasses,这个对象存放着当前类加载器加载的代理类的Class类实例,下面的方法本质,就是从这个generatedClasses里面匹配
//只要代理类的classLoader存在,这些代理类就是可以重用的
//通过generatedClasses缓存是获取代理类的唯一方法
private final LoadingCache<AbstractClassGenerator, Object, Object> generatedClasses;
// ...
public Object get(AbstractClassGenerator gen, boolean useCache) {
//默认是使用缓存的,可以通过以下属性设置不使用缓存
//System.setProperty("cglib.useCache", "false")
if (!useCache) {
return gen.generate(AbstractClassGenerator.ClassLoaderData.this);
} else {
//从generatedClasses中获取Class对象
Object cachedValue = generatedClasses.get(gen);
return gen.unwrapCachedValue(cachedValue);
}
}
再来看看LoadingCache这个类,需要重点理解这三个字段:
//K:AbstractClassGenerator 这里指Enhancer类
//KK:Object 这里指前面生成key的类
//V:Object 这里指代理类的Class类
public class LoadingCache<K, KK, V> {
//通过key可以拿到代理类的Class实例
protected final ConcurrentMap<KK, Object> map;
//通过loader.apply(Enhancer实例)可以获得代理类的Class实例
protected final Function<K, V> loader;
//通过keyMapper.apply(Enhancer实例)可以获得key
protected final Function<K, KK> keyMapper;
//·······
}
在get方法中,通过key生成的cachKey去缓存中查找,如果没找到,则创建Class实例,并放入缓存map中:
public V get(K key) {
//通过key生成cacheKey
final KK cacheKey = keyMapper.apply(key);
//通过cacheKey查找缓存
Object v = map.get(cacheKey);
if (v != null && !(v instanceof FutureTask)) {
return (V) v;
}
//如果没找到,就创建Class实例,并放入缓存
return createEntry(key, cacheKey, v);
}
3.生成代理类Class
//LoadingCache.createEntry()
//省略了无关代码
protected V createEntry(final K key, KK cacheKey, Object v) {
//创建Class实例
V result = loader.apply(key);
//放入缓存中
map.put(cacheKey, result);
return result;
}
loader是一个Function,是创建LoadingCache的时候通过构造器传入的,loader是在AbstractClassGenerator的内部类ClassLoaderData中创建的:
//AbstractClassGenerator$ClassLoaderData的构造函数
Function<AbstractClassGenerator, Object> load =
new Function<AbstractClassGenerator, Object>() {
public Object apply(AbstractClassGenerator gen) {
//生成一个class的字节码
Class klass = gen.generate(ClassLoaderData.this);
return gen.wrapCachedClass(klass);
}
};
generatedClasses = new LoadingCache<AbstractClassGenerator, Object, Object>(GET_KEY, load);
4.创建代理对象
创建了代理类的Class对象后,通过AbstractClassGenerator.firstInstance(Class type)来创建代理类的实例,该方法是一个abstract方法,实现在Enhancer中:
//Enhancer
protected Object firstInstance(Class type) throws Exception {
if (classOnly) {
return type;
} else {
//会执行到这里
return createUsingReflection(type);
}
}
/**
* Instantiates a proxy instance and assigns callback values.
* Implementation detail: java.lang.reflect instances are not cached, so this method should not
* be used on a hot path.
* This method is used when {@link #setUseCache(boolean)} is set to {@code false}.
*
* @param type class to instantiate
* @return newly created instance
*/
private Object createUsingReflection(Class type) {
setThreadCallbacks(type, callbacks);
try{
if (argumentTypes != null) {
return ReflectUtils.newInstance(type, argumentTypes, arguments);
} else {
return ReflectUtils.newInstance(type);
}
} finally {
// clear thread callbacks to allow them to be gc'd
setThreadCallbacks(type, null);
}
}
最后就是通过反射创建了代理类的实例。
调用代理对象的方法 helloProxy.sayHello("Doris");
1.代理类的源码分析
从测试结果可以看到,对于helloProxy.sayHello("Doris");的调用,最终调用到了MyInterceptor.intercept()方法上,为什么呢?先看下debug模式下的helloProxy的类型:
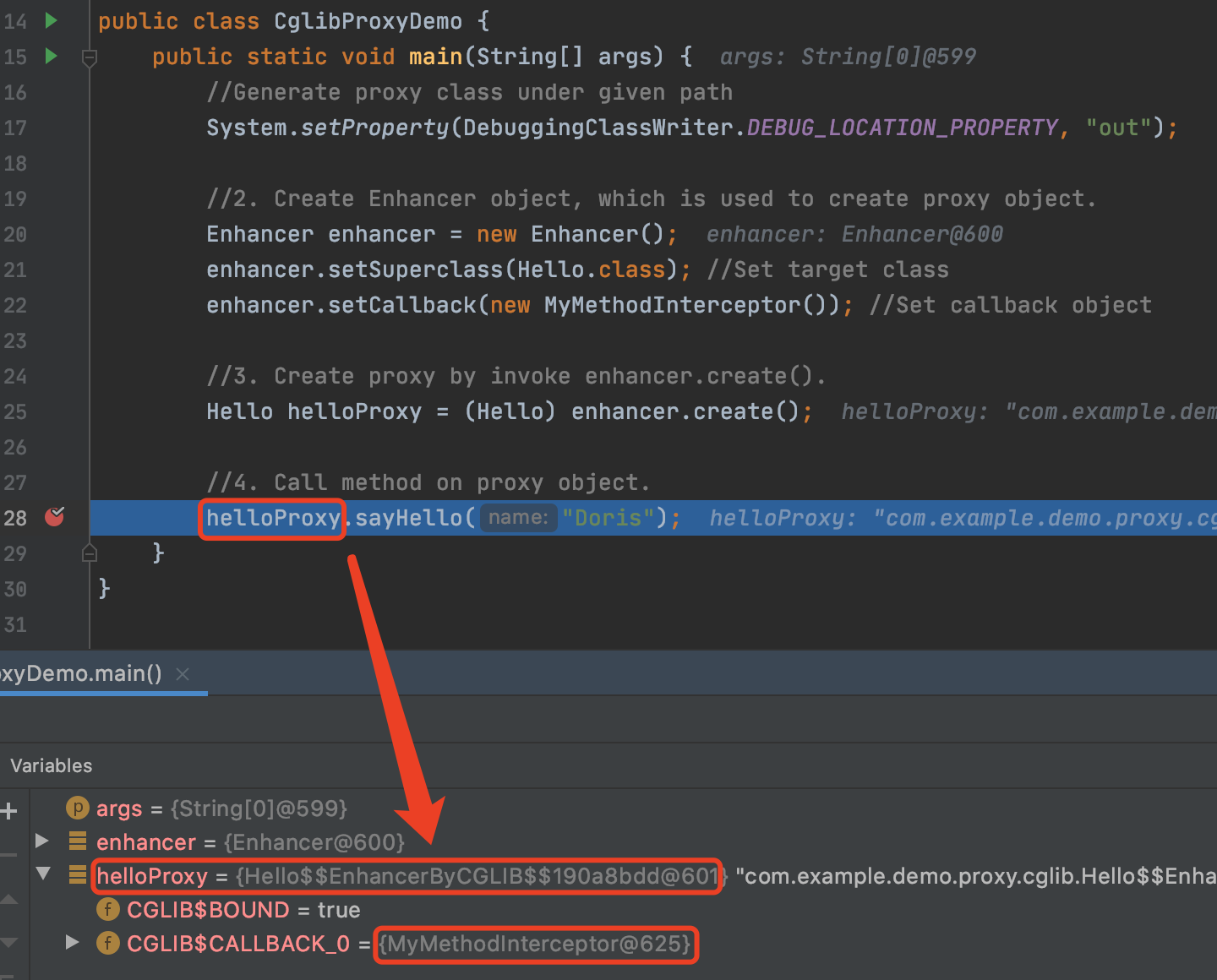
可以看到,helloProxy对象的类型是“Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd”,这是一个CGLIB生成的用于代理Hello的代理类,并且其CGLIB$CALLBACK_0属性就是我们通过enhancer.setCallback()设置的MyMethodInterceptor。
为了便于分析,我们通过第一句保留了CGLIB生成的动态代理的文件在项目根目录的out文件夹下:
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY, "out");

在IDEA中打开打开这个生成的代理类:
package com.example.demo.proxy.cglib;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import net.sf.cglib.core.ReflectUtils;
import net.sf.cglib.core.Signature;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Callback;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.Factory;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import net.sf.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
//可以看到这个代理类是Hello的子类,并且实现了Factory接口,该接口主要用于实例化对象和设置回调函数。
//生成的类名的规则:被代理ClassName + "$$" + ClassGeneratorName + "ByCGLIB" + "$$" + key的hashCode
public class Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd extends Hello implements Factory {
private boolean CGLIB$BOUND;
public static Object CGLIB$FACTORY_DATA;
private static final ThreadLocal CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS;
private static final Callback[] CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
private MethodInterceptor CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
private static Object CGLIB$CALLBACK_FILTER;
//这里有很多属性,基本上一个Method对应一个MethodProxy
private static final Method CGLIB$sayHello$0$Method;//被代理的sayHello()方法
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$sayHello$0$Proxy;//代理的sayHello()方法
private static final Object[] CGLIB$emptyArgs;
private static final Method CGLIB$equals$1$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$toString$2$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy;
private static final Method CGLIB$clone$4$Method;
private static final MethodProxy CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
// 静态代码块,主要是通过【反射】获取了以下方法的字节码:
// Object.equals()
// Object.toString()
// Object.hashCode()
// Object.clone()
// Hello.sayHello()
// 并为这些方法创建对应的MethodProxy
static void CGLIB$STATICHOOK1() {
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS = new ThreadLocal();
CGLIB$emptyArgs = new Object[0];
//代理类Class对象
Class var0 = Class.forName("com.example.demo.proxy.cglib.Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd");
//被代理类Class对象
Class var1;
//被代理类var1在这一行被赋值为java.lang.Object
Method[] var10000 = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"equals", "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "toString", "()Ljava/lang/String;", "hashCode", "()I", "clone", "()Ljava/lang/Object;"}, (var1 = Class.forName("java.lang.Object")).getDeclaredMethods());
CGLIB$equals$1$Method = var10000[0];
CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z", "equals", "CGLIB$equals$1");
CGLIB$toString$2$Method = var10000[1];
CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()Ljava/lang/String;", "toString", "CGLIB$toString$2");
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Method = var10000[2];
CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()I", "hashCode", "CGLIB$hashCode$3");
CGLIB$clone$4$Method = var10000[3];
CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "()Ljava/lang/Object;", "clone", "CGLIB$clone$4");
//被代理类var1在这一行被赋值为com.example.demo.proxy.cglib.Hello
CGLIB$sayHello$0$Method = ReflectUtils.findMethods(new String[]{"sayHello", "(Ljava/lang/String;)V"}, (var1 = Class.forName("com.example.demo.proxy.cglib.Hello")).getDeclaredMethods())[0];
//这里创建了sayHello方法的代理
CGLIB$sayHello$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", "sayHello", "CGLIB$sayHello$0");
}
//这个方法就是调用目标类的sayHello()方法
final void CGLIB$sayHello$0(String var1) {
super.sayHello(var1);
}
//这个方法就是sayHello()方法在代理对象中的实现,即在我们样例中helloProxy.sayHello()调用的方法
public final void sayHello(String var1) {
MethodInterceptor var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
//var10000就是样例中enhancer.setCallback(new MyMethodInterceptor());设置的方法拦截器
if (var10000 != null) {
//如果方法拦截器存在,就调用它的interceptor方法。就会调用MyMethodInterceptor.intercept()方法
var10000.intercept(this, CGLIB$sayHello$0$Method, new Object[]{var1}, CGLIB$sayHello$0$Proxy);
} else {
//如果方法拦截器不存在,就只执行目标类的sayHello()方法
super.sayHello(var1);
}
}
//...
//省略了equals, toString, hashCode, clone等方法的实现,逻辑都是类似的:
//如果方法拦截器存在,就调用拦截器的intercept方法,否则直接调用父类的方法
//...
public static MethodProxy CGLIB$findMethodProxy(Signature var0) {
String var10000 = var0.toString();
switch(var10000.hashCode()) {
case -508378822:
if (var10000.equals("clone()Ljava/lang/Object;")) {
return CGLIB$clone$4$Proxy;
}
break;
case 771401912:
if (var10000.equals("sayHello(Ljava/lang/String;)V")) {
return CGLIB$sayHello$0$Proxy;
}
break;
case 1826985398:
if (var10000.equals("equals(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z")) {
return CGLIB$equals$1$Proxy;
}
break;
case 1913648695:
if (var10000.equals("toString()Ljava/lang/String;")) {
return CGLIB$toString$2$Proxy;
}
break;
case 1984935277:
if (var10000.equals("hashCode()I")) {
return CGLIB$hashCode$3$Proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
//无参构造函数
public Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd() {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_THREAD_CALLBACKS(Callback[] var0) {
CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.set(var0);
}
public static void CGLIB$SET_STATIC_CALLBACKS(Callback[] var0) {
CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS = var0;
}
private static final void CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(Object var0) {
Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd var1 = (Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd)var0;
if (!var1.CGLIB$BOUND) {
var1.CGLIB$BOUND = true;
Object var10000 = CGLIB$THREAD_CALLBACKS.get();
if (var10000 == null) {
var10000 = CGLIB$STATIC_CALLBACKS;
if (var10000 == null) {
return;
}
}
var1.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0 = (MethodInterceptor)((Callback[])var10000)[0];
}
}
//...
//省略了实现的Factory接口的方法
//...
//调用静态代码块,完成Method和MethodProxy的初始化
static {
CGLIB$STATICHOOK1();
}
}
可以看到,当在代理对象上调用sayHello()方法时,会先检查这个代理对象是否有MethodInterceptor,如果有,则调用其intercept方法,没有则直接调用目标对象的sayHello()方法。这里就进入到了MyMethodInterceptor.intercept()方法,打印了这句话:
>>>> Before method invocation
2. MethodProxy.invokeSuper()
这里的MethodProxy是在代理类的静态块CGLIB$STATICHOOK1中通过创建的:
//Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd
CGLIB$sayHello$0$Proxy = MethodProxy.create(var1, var0, "(Ljava/lang/String;)V", "sayHello", "CGLIB$sayHello$0");
//MethodProxy
public static MethodProxy create(Class c1, Class c2, String desc, String name1, String name2) {
MethodProxy proxy = new MethodProxy();
proxy.sig1 = new Signature(name1, desc);
proxy.sig2 = new Signature(name2, desc);
//创建了createInfo属性
proxy.createInfo = new MethodProxy.CreateInfo(c1, c2);
return proxy;
}
这里创建了proxy对象的createInfo属性,接下来会在invokeSuper()方法中调用init()方法的时候,用该属性来创建FastClass类
public Object invokeSuper(Object obj, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//初始化,创建了两个FastClass类对象,并根据原来的方法签名得到方法索引
init();
//这个对象持有两个FastClass类对象和方法的索引,见下方FastClassInfo类
MethodProxy.FastClassInfo fci = fastClassInfo;
//f2是代理对象的FastClass,这里是调用代理对象上索引为i2的方法
return fci.f2.invoke(fci.i2, obj, args);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
throw e.getTargetException();
}
}
private void init() {
if (fastClassInfo == null) {
synchronized (initLock) {
if (fastClassInfo == null) {
//用createInfo属性来创建FastClassInfo
MethodProxy.CreateInfo ci = createInfo;
MethodProxy.FastClassInfo fci = new MethodProxy.FastClassInfo();
//helper方法用ASM框架生成了两个FastClass类
fci.f1 = helper(ci, ci.c1);//目标类的FastClass
fci.f2 = helper(ci, ci.c2);//代理类的FastClass
//分别从FastClass中获取指定签名的方法
fci.i1 = fci.f1.getIndex(sig1);//在目标类的FastClass中获取方法索引
fci.i2 = fci.f2.getIndex(sig2);//在代理类的FastClass中获取方法索引
//将fci赋值给全局变量fastClassInfo
fastClassInfo = fci;
createInfo = null;
}
}
}
}
private static class FastClassInfo {
//目标类的FastClass类
FastClass f1;
//代理类的FastClass类
FastClass f2;
//目标类FastClass中的方法索引
int i1;
//代理类FastClass中的方法索引
int i2;
}
这里主要是通过MethodProxy.init()方法为目标类和代理类分别创建了FastClass,然后初始化了一个FastClassInfo对象(该对象持有两个FastClass以及FastClass中对于该方法的索引),最后在代理对象上调用了invoke方法。
3.FastClass类的代码分析
来看看代理类的FastClass(就是CGLIB生成的文件名最长的类),它是net.sf.cglib.reflect.FastClass的子类,主要用于给指定的类(这里是代理类)建立方法索引,避免每次使用反射去调用方法。该类里面主要是通过方法签名(Signature)获取方法索引(index)的方法,以及通过方法索引(index)调用方法的方法。
package com.example.demo.proxy.cglib;
import com.example.demo.proxy.cglib.Hello..EnhancerByCGLIB..190a8bdd;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import net.sf.cglib.core.Signature;
import net.sf.cglib.reflect.FastClass;
public class Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd$$FastClassByCGLIB$$cbc4a17e extends FastClass {
public Hello$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$190a8bdd$$FastClassByCGLIB$$cbc4a17e(Class var1) {
super(var1);
}
//通过方法签名获取方法的索引,该索引将用于快速调用方法(下面invoke方法中的case)
public int getIndex(Signature var1) {
String var10000 = var1.toString();
switch(var10000.hashCode()) {
case 771401912:
if (var10000.equals("sayHello(Ljava/lang/String;)V")) {
return 14;
}
break;
//...省略其他的case
}
return -1;
}
//通过方法名和参数类型获取方法的索引。比如var1="sayHello", var2=[java.lang.String]
/**
* Return the index of the matching method. The index may be used
* later to invoke the method with less overhead. If more than one
* method matches (i.e. they differ by return type only), one is
* chosen arbitrarily.
* @see #invoke(int, Object, Object[])
* @param name the method name
* @param parameterTypes the parameter array
* @return the index, or <code>-1</code> if none is found.
*/
public int getIndex(String var1, Class[] var2) {
switch(var1.hashCode()) {
case -2012993625:
if (var1.equals("sayHello")) {
switch(var2.length) {
case 1:
if (var2[0].getName().equals("java.lang.String")) {
return 14;
}
}
}
break;
//...省略其他的case
}
return -1;
}
//通过参数类型获取构造器的索引,该索引用于稍后创建实例(下面newInstance方法中的case)
/**
* Return the index of the matching constructor. The index may be used
* later to create a new instance with less overhead.
* @see #newInstance(int, Object[])
* @param parameterTypes the parameter array
* @return the constructor index, or <code>-1</code> if none is found.
*/
public int getIndex(Class[] var1) {
switch(var1.length) {
//只有一个默认的无参构造器,因此只有一个case 0
case 0:
return 0;
default:
return -1;
}
}
//调用方法(注释来自FastClass类)
/**
* Invoke the method with the specified index.
* @see getIndex(name, Class[])
* @param index the method index
* @param obj the object the underlying method is invoked from
* @param args the arguments used for the method call
* @throws java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException if the underlying method throws an exception
*/
public Object invoke(int var1, Object var2, Object[] var3) throws InvocationTargetException {
190a8bdd var10000 = (190a8bdd)var2;
int var10001 = var1;
try {
switch(var10001) {
//这里的case的情况都由getIndex(Signature var1)方法
//或getIndex(String var1, Class[] var2)方法返回
case 14:
var10000.sayHello((String)var3[0]);
return null;
//...省略其他的case
}
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new InvocationTargetException(var4);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot find matching method/constructor");
}
//通过构造器实例化对象(注释来自FastClass类)
/**
* Create a new instance using the specified constructor index and arguments.
* @see getIndex(Class[])
* @param index the constructor index
* @param args the arguments passed to the constructor
* @throws java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException if the constructor throws an exception
*/
public Object newInstance(int var1, Object[] var2) throws InvocationTargetException {
190a8bdd var10000 = new 190a8bdd;
190a8bdd var10001 = var10000;
int var10002 = var1;
try {
switch(var10002) {
case 0:
//构造器是0个参数,表示通过无参构造器创建对象
var10001.<init>();
return var10000;
}
} catch (Throwable var3) {
throw new InvocationTargetException(var3);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot find matching method/constructor");
}
/**
* Returns the maximum method index for this class.
*/
public int getMaxIndex() {
return 20;
}
}
可以看到,对于proxy.invokeSuper()的调用,实际上调用了fci.f2.invoke(fci.i2, obj, args)。而fci.i2 = fci.f2.getIndex(sig2); 注意这里的sig2是指CGLIB$sayHello$0()这个方法,即代理对象中用于调用目标对象sayHello()的方法。
所以整个调用流程为:
1.通过sayHello()的方法签名,在代理类的FastClass中找到**CGLIB$sayHello$0()**方法的索引。
2.调用fci.f2.invoke()方法,因此直接调用代理对象的**CGLIB$sayHello$0()**方法,于是间接调用到了Hello.sayHello()方法,输出了下面这句:
Hello Doris
最后继续在MyMethodInterceptor中输出了
>>>> After method invocation
【全文完】
=========================分隔线=====================================
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/106069224
=========================分隔线=====================================











