写了vue项目和小程序,发现二者有许多相同之处,在此想总结一下二者的共同点和区别。
一、生命周期
先贴两张图:
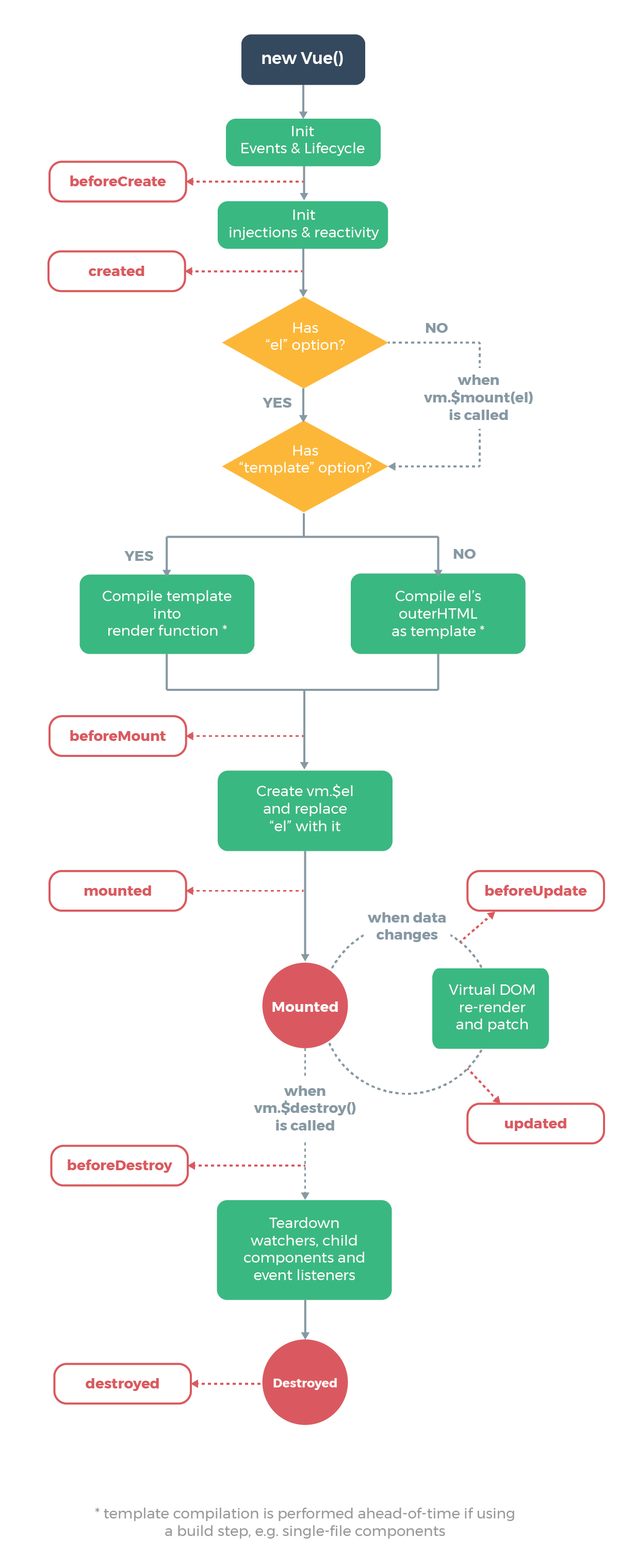
vue生命周期
小程序生命周期
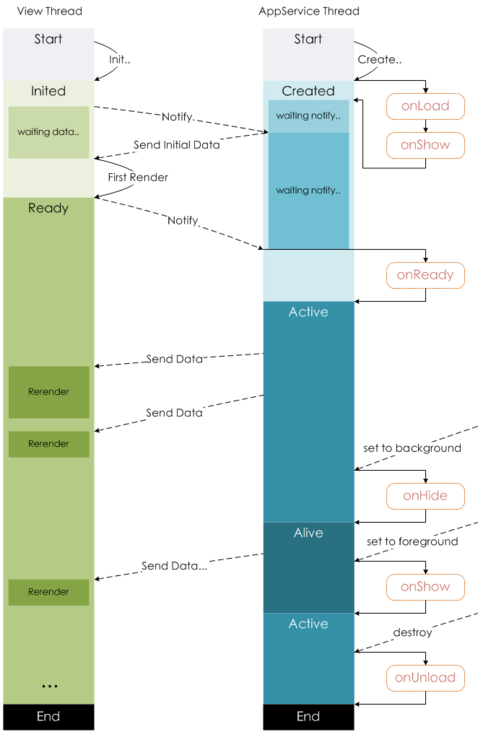
相比之下,小程序的钩子函数要简单得多。
vue的钩子函数在跳转新页面时,钩子函数都会触发,但是小程序的钩子函数,页面不同的跳转方式,触发的钩子并不一样。
onLoad: 页面加载 一个页面只会调用一次,可以在onLoad中获取打开当前页面所调用的query参数。onShow: 页面显示 每次打开页面都会调用一次。onReady: 页面初次渲染完成 一个页面只会调用一次,代表页面已经准备妥当,可以和视图层进行交互。 对界面的设置如wx.setNavigationBarTitle请在onReady之后设置。详见生命周期onHide: 页面隐藏 当navigateTo或底部tab切换时调用。onUnload: 页面卸载 当redirectTo或navigateBack的时候调用。
数据请求
在页面加载请求数据时,两者钩子的使用有些类似,vue一般会在created或者mounted中请求数据,而在小程序,会在onLoad或者onShow中请求数据。
二、数据绑定
VUE:vue动态绑定一个变量的值为元素的某个属性的时候,会在变量前面加上冒号:,例:
<img :src="imgSrc"/> 小程序:绑定某个变量的值为元素属性时,会用两个大括号括起来,如果不加括号,为被认为是字符串。例:
<image src="{{imgSrc}}"></image> 三、列表渲染
直接贴代码,两者还是有些相似 vue:
<ul id="example-1">
<li v-for="item in items">
{{ item.message }}
</li>
</ul>
var example1 = new Vue({
el: '#example-1',
data: {
items: [
{ message: 'Foo' },
{ message: 'Bar' }
]
}
}) 小程序:
Page({
data: {
items: [
{ message: 'Foo' },
{ message: 'Bar' }
]
}
})
<text wx:for="{{items}}">{{item}}</text> 四、显示与隐藏元素
vue中,使用v-if 和v-show控制元素的显示和隐藏
小程序中,使用wx-if和hidden控制元素的显示和隐藏
五、事件处理
vue:使用v-on:event绑定事件,或者使用@event绑定事件,例如:
<button v-on:click="counter += 1">Add 1</button>
<button v-on:click.stop="counter+=1">Add1</button> //阻止事件冒泡 小程序中,全用bindtap(bind+event),或者catchtap(catch+event)绑定事件,例如:
<button bindtap="noWork">明天不上班</button>
<button catchtap="noWork">明天不上班</button> //阻止事件冒泡 六、数据双向绑定
1.设置值
在vue中,只需要再表单元素上加上v-model,然后再绑定data中对应的一个值,当表单元素内容发生变化时,data中对应的值也会相应改变,这是vue非常nice的一点。
<div id="app">
<input v-model="reason" placeholder="填写理由" class='reason'/>
</div>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {
reason:''
}
}) 但是在小程序中,却没有这个功能。那怎么办呢? 当表单内容发生变化时,会触发表单元素上绑定的方法,然后在该方法中,通过this.setData({key:value})来将表单上的值赋值给data中的对应值。 下面是代码,可以感受一下:
<input bindinput="bindReason" placeholder="填写理由" class='reason' value='{{reason}}' name="reason" />
Page({
data:{
reason:''
},
bindReason(e) {
this.setData({
reason: e.detail.value
})
}
}) 当页面表单元素很多的时候,更改值就是一件体力活了。和小程序一比较,vue的v-model简直爽的不要不要的。
2.取值
vue中,通过this.reason取值
小程序中,通过this.data.reason取值
七、绑定事件传参
在vue中,绑定事件传参挺简单,只需要在触发事件的方法中,把需要传递的数据作为形参传入就可以了,例如:
<button @click="say('明天不上班')"></button>
new Vue({
el: '#app',
methods:{
say(arg){
consloe.log(arg)
}
}
}) 在小程序中,不能直接在绑定事件的方法中传入参数,需要将参数作为属性值,绑定到元素上的data-属性上,然后在方法中,通过e.currentTarget.dataset.*的方式获取,从而完成参数的传递,很麻烦有没有...
<view class='tr' bindtap='toApprove' data-id="{{item.id}}"></view>
Page({
data:{
reason:''
},
toApprove(e) {
let id = e.currentTarget.dataset.id;
}
}) 八、父子组件通信
1.子组件的使用
在vue中,需要:
- 编写子组件
- 在需要使用的父组件中通过
import引入 - 在
vue的components中注册 - 在模板中使用
//子组件 bar.vue
<template>
<div class="search-box">
<div @click="say" :title="title" class="icon-dismiss"></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
props:{
title:{
type:String,
default:''
}
}
},
methods:{
say(){
console.log('明天不上班');
this.$emit('helloWorld')
}
}
</script>
// 父组件 foo.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<bar :title="title" @helloWorld="helloWorld"></bar>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Bar from './bar.vue'
export default{
data(){
return{
title:"我是标题"
}
},
methods:{
helloWorld(){
console.log('我接收到子组件传递的事件了')
}
},
components:{
Bar
}
</script> 在小程序中,需要:
编写子组件
在子组件的
json文件中,将该文件声明为组件{ "component": true }在需要引入的父组件的
json文件中,在usingComponents填写引入组件的组件名以及路径"usingComponents": { "tab-bar": "../../components/tabBar/tabBar" }在父组件中,直接引入即可
<tab-bar currentpage="index"></tab-bar>具体代码:
// 子组件 <!--components/tabBar/tabBar.wxml--> <view class='tabbar-wrapper'> <view class='left-bar {{currentpage==="index"?"active":""}}' bindtap='jumpToIndex'> <text class='iconfont icon-shouye'></text> <view>首页</view> </view> <view class='right-bar {{currentpage==="setting"?"active":""}}' bindtap='jumpToSetting'> <text class='iconfont icon-shezhi'></text> <view>设置</view> </view> </view>
2.父子组件间通信
在vue中
父组件向子组件传递数据,只需要在子组件通过v-bind传入一个值,在子组件中,通过props接收,即可完成数据的传递,示例:
// 父组件 foo.vue
<template>
<div class="container">
<bar :title="title"></bar>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Bar from './bar.vue'
export default{
data(){
return{
title:"我是标题"
}
},
components:{
Bar
}
</script>
// 子组件bar.vue
<template>
<div class="search-box">
<div :title="title" ></div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
props:{
title:{
type:String,
default:''
}
}
}
</script> 子组件和父组件通信可以通过this.$emit将方法和数据传递给父组件。
在小程序中
父组件向子组件通信和vue类似,但是小程序没有通过v-bind,而是直接将值赋值给一个变量,如下:
<tab-bar currentpage="index"></tab-bar>
此处, “index”就是要向子组件传递的值 在子组件properties中,接收传递的值
properties: {
// 弹窗标题
currentpage: { // 属性名
type: String, // 类型(必填),目前接受的类型包括:String, Number, Boolean, Object, Array, null(表示任意类型)
value: 'index' // 属性初始值(可选),如果未指定则会根据类型选择一个
}
} 子组件向父组件通信和vue也很类似,代码如下:
//子组件中
methods: {
// 传递给父组件
cancelBut: function (e) {
var that = this;
var myEventDetail = { pickerShow: false, type: 'cancel' } // detail对象,提供给事件监听函数
this.triggerEvent('myevent', myEventDetail) //myevent自定义名称事件,父组件中使用
},
}
//父组件中
<bar bind:myevent="toggleToast"></bar>
// 获取子组件信息
toggleToast(e){
console.log(e.detail)
} 如果父组件想要调用子组件的方法
vue会给子组件添加一个ref属性,通过this.$refs.ref的值便可以获取到该子组件,然后便可以调用子组件中的任意方法,例如:
//子组件
<bar ref="bar"></bar>
//父组件
this.$ref.bar.子组件的方法 小程序是给子组件添加id或者class,然后通过this.selectComponent找到子组件,然后再调用子组件的方法,示例:
//子组件
<bar id="bar"></bar>
// 父组件
this.selectComponent('#id').syaHello() 小程序父组件改变子组件样式
1.父组件将style传入子组件 2.父组件传入变量控制子组件样式 3.在父组件样式中,在子组件类名前面加上父组件类名
<view class='share-button-container' bindtap='handleShareBtn'>
<share-button product="{{goodProduct}}" type="1" back-color="#fff" fore-color="#9e292f" bind:error="on_error" />
</view>
.share-button-container .button--btn-navigator__hover{
background: #fff;
}